¶ Quick Start
¶ Matrix routing fundamentals
A matrix-based switching system consists of
- An X by Y grid of switching elements
- X column conductors
- Y row conductors
The switching elements are placed at the crosspoints between row and column conductors. A switching element at a crosspoint can be in one of two states:
- closed
- open
When the switching element is closed, it creates a connection between the row and column conductors meeting at the crosspoint.
There are many ways that a general matrix switching system can be used to create circuits, depending on exact application, but only one way stands out as the most clean and efficient way to create arbitrary connections. It is descried below.
A matrix switching system typically will have one short dimension and one long dimension. Designate the long axis (X-axis) to switched resources and short axis (Y-axis) to routing. This is going to be explained further.
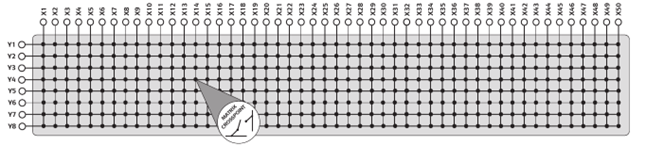
¶ Matrix routing procedure
-
Split up your circuit into nets (groups of connected nodes).
-
Physically attach device nodes to X columns
-
Designate a unique Y row to each net in the circuit you want to route
-
To implement a net, close all crosspoints at the intersections of each node's X column and the Y row of the net